Olive Oil in Clinical Nutrition: Strategies for Lipid and Glycemic Management
Olive oil is a functional fat that promotes cardiometabolic health by enhancing lipid and glycemic profiles through its MUFA and phenolic compounds, supporting LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides, inflammation control, endothelial function, and postprandial lipemia. Extra virgin olive oil, rich in polyphenols, is best for drizzling and low-heat cooking, preserving its antioxidant and metabolic benefits. Olive oil for Indian Cooking features a higher smoke point, making it suitable for deep-frying, stir-frying, and everyday meals. Classic olive oil, with its robust flavor and high smoke point, is ideal for Mediterranean and continental dishes, allowing practical, heart-healthy culinary use._page-0001.jpg)
_page-0002.jpg)
_page-0003.jpg)
Related Content

Video
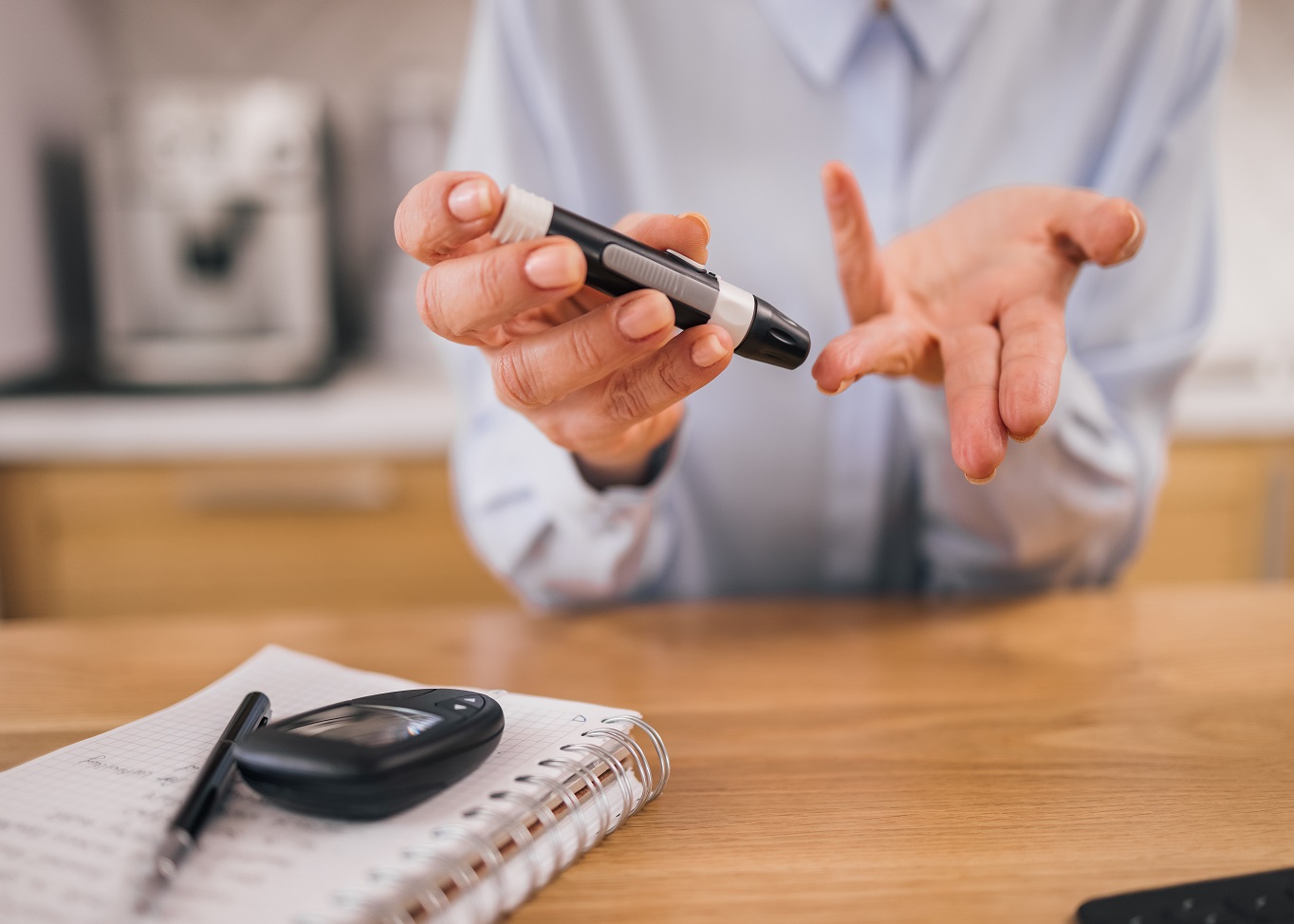
Blood Sugar: Balance Starts in the Kitchen
With rising diabetes in India, sugar reduction alone is not enough-cooking oil choice matters. Olive oil, rich in MUFAs and phenolic compounds, may help prevent and manage type 2 diabetes by lowering glycemic load, reducing insulin secretion, and improving insulin sensitivity. Within a Mediterranean-style diet, EVOO improves glucose markers, inflammation and lipid levels. EVOO suits salads and light cooking, while high-smoke point olive oil variants fit Indian dishes such as curries, sabzi and parathas.
.jpg)
Video
Topic: Home-Cooked Food, Yet Feeling Acidic or Sluggish?
Even with healthy habits, many people experience bloating. While diet influences gut health, choosing the right cooking oil is often overlooked. Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO), rich in MUFAs and polyphenols, offers antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits central to the Mediterranean diet. Olive oils higher–smoke point variants suit heart-friendly Indian cooking, including curries, sabzi and parathas, while EVOO works well for salads and light cooking. Using the right oil may ease acidity, improve digestion, and enhance comfort.

Video
Cooking Oil, Heart Health & Cholesterol
Olive oil, central to the Mediterranean diet, provides monounsaturated fats, phenolic compounds, vitamin E, and bioactive lipids with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. Evidence shows it can reduce LDL, triglycerides, and improve HDL profile. Extra-virgin olive oil may lower cardiovascular risk by nearly 31% and is ideal for spreading, salad dressing and low-heat cooking. High–smoke point olive oil variants make it versatile for Indian dishes such as curries, sabzi and tadkas without compromising heart health.
.jpg)
Video
Blood Sugar Balance Ki Shuruwaat Kitchen Se
Diabetes involves more than sugar intake-cooking oil also affects glucose control. Olive oil’s MUFAs and phenolic compounds may help prevent or manage type 2 diabetes by lowering glycemic load, reducing insulin secretion and improving insulin sensitivity. Salads dressing and drizzling are best done using EVOO whereas Indian dishes like deep fry, parathas, curry and sabzi are better cooked using high–smoke point olive oil variants. Both varieties support healthier gut microbiota, better carbohydrate metabolism and reduced insulin resistance.
 (1).jpg)
Video
Ghar ka Khana, Fir Bhi Acidity?
Despite eating home-cooked meals, many still experience acidity or bloating. Cooking oil selection plays a key role in gut comfort. Olive oil offers MUFAs, vitamin E and polyphenols that influence taste, aroma and digestive function. EVOO, with a lower smoke point, is best for salads dressing, drizzling and light cooking. High–smoke point olive oil variants suit everyday Indian preparations such as deep fry, sabzi, curry and parathas. Choosing such oils may improve digestion, reduce acidity and enhance energy.
.jpg)
Video
Dil aur Cholesterol ke Liye Chune Sahi Tel
Olive oil is the primary fat in the Mediterranean diet, linked to longer life and lower heart disease risk. Beyond rich MUFA content, it provides vitamin E, phenolic compounds, and bioactive lipids that improve HDL function, reduce LDL, and support cholesterol metabolism. Mediterranean diet enriched with EVOO lowers long-term heart risk. EVOO suits toast, salads and light cooking, while higher–smoke point olive oil variants work for deep fry, parathas, curry and sabzi.

Article
Heart-Healthy Choices: Experts Highlight the Power of Functional Fats and Lifestyle
Renowned clinicians emphasize that the quality of dietary fats plays a decisive role in cardiovascular and metabolic health. Incorporating MUFA-rich oils such as olive oil, alongside balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, supports heart function, improves insulin sensitivity, and strengthens long-term disease prevention through small, evidence-based lifestyle modifications.
Infographic
The MUFA Advantage: Olive Oil’s Role in Hypertension and Diabetes Management
Functional fats rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), such as olive oil, support cardiovascular, hypertensive, and diabetic health. Regular consumption improves insulin sensitivity, reduces fasting glucose and HbA1c, and lowers blood pressure. Integrating olive oil into a balanced Mediterranean-style diet fosters long-term cardiometabolic protection through evidence-based nutritional intervention.

